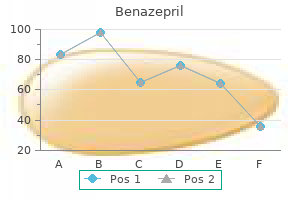
Benazepril
"Generic benazepril 10mg on-line, medications like tramadol".
By: Y. Jensgar, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, University of Kentucky College of Medicine
Trophoblastic cells proliferate and type the syncytiotrophoblast medications emt can administer generic 10mg benazepril amex, whose function is to treatment naive definition discount benazepril online master card permit the blastocyst to treatment question benazepril 10 mg amex penetrate deep into the endometrium. The timetable is predicated on the variety of days after ovulation and consists of the next steps: 1. Fertilization of the ovum takes place within 24 hours of ovulation, in a distal portion of the oviduct called the ampulla. Once a sperm penetrates the ovum, the second polar body is extruded and the fertilized ovum begins to divide. Four days after ovulation the fertilized ovum, the blastocyst, with approximately a hundred cells, arrives in the uterine cavity. Days After Ovulation 0 day 1 day four days 5 days 6 days eight days 10 days the period of being pregnant is, by convention, counted from the date of the final menstrual interval. Pregnancy lasts approximately 40 weeks from the onset of the final menstrual interval, or 38 weeks from the date of the final ovulation. Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters, every of which corresponds to approximately thirteen weeks. Parturition Pr og E io str l Parturition, the delivery of the fetus, occurs approximately 40 weeks after the onset of the final menstrual interval. The mechanism of parturition is unclear, though roles for estrogen, progesterone, cortisol, oxytocin, prostaglandins, relaxin, and catecholamines have been proposed. The following events occur close to term and may contribute to parturition: 40 10 20 Weeks of being pregnant 30. Once the fetus reaches a critical measurement, distention of the uterus increases its contractility. Uncoordinated contractions, often known as Braxton Hicks contractions, start approximately 1 month before parturition. Near term, the fetal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is activated and the fetal adrenal cortex produces vital quantities of cortisol. Cortisol increases the estrogen/progesterone ratio, which increases the sensitivity of the uterus to contractile stimuli. Recall that estrogen and progesterone have opposite results on uterine contractility: Estrogen increases contractility, and progesterone decreases it. Thus the increasing estrogen/progesterone ratio stimulates local prostaglandin manufacturing, which plays a number of roles in labor and delivery. Evidence signifies that the uterine oxytocin receptors are up-regulated towards the tip of gestation. It can also be known that dilation of the cervix, as occurs through the progression of labor, stimulates oxytocin secretion. During the second and third trimesters, the placenta, in live performance with the mother and the fetus, assumes accountability for manufacturing of steroid hormones. The pathways for the synthesis of progesterone and estrogen are proven in Figure 10. Progesterone is produced by the placenta as follows: Cholesterol enters the placenta from the maternal circulation. In the placenta, ldl cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone, which then is converted to progesterone. Estriol, the major type of estrogen throughout being pregnant, is produced through a coordinated interplay of the mother and the placenta, and, importantly, requires the fetus. Again, ldl cholesterol is equipped to the placenta from the maternal circulation and is converted to pregnenolone in the placenta. Estriol synthesis requires the placenta, the fetal adrenal gland, and the fetal liver. In the primary stage, uterine contractions originating at the fundus and sweeping downward transfer the head of the fetus towards the cervix and progressively widen and skinny the cervix. In the second stage, the fetus is compelled through the cervix and delivered through the vagina.
Increased circulating ranges of the intercourse steroid hormones are then responsible for the appearance of the secondary intercourse traits at puberty symptoms hyperthyroidism cheap benazepril online amex. The onset of the maturational course of at puberty is genetically programmed medications with weight loss side effect cheap 10 mg benazepril, and familial patterns are evident schedule 9 medications buy benazepril 10 mg low cost. For example, the age at menarche (the onset of menses) is similar between moms and daughters. The central nervous system and nutritional status might alter the process; for example, excessive stress or caloric deprivation in girls delays the onset of puberty. In support of a task for melatonin is the observation that removal of the pineal gland precipitates early puberty. Characteristics of Puberty As noted, the biologic events at puberty are set in motion by the onset of pulsatile exercise within the hypothalamicanterior pituitary axis. In turn, this pulsatile, or bursting, exercise causes the testes and ovaries to secrete their respective intercourse hormones, testosterone and estrogen, that are responsible for the development of the secondary intercourse traits. In boys, puberty is related to activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, Leydig cell proliferation within the testes, and increased synthesis and secretion of testosterone by the Leydig cells. There is growth of the testes, largely because of an increased number of seminiferous tubules. There is a pronounced linear growth spurt, and the epiphyses shut when grownup top is attained. In girls, puberty is also related to the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, which drives the synthesis of estradiol by the ovaries. The first 466 · Physiology observable sign of puberty in girls is budding of the breasts, which is adopted in roughly 2 years by menarche, the onset of menstrual cycles. The growth spurt and closure of the epiphyses typically start and end earlier in girls than in boys. The appearance of pubic and axillary hair, called adrenarche, precedes menarche and is dependent on increased secretion of adrenal androgens. Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis occurs constantly all through the reproductive lifetime of the male, from puberty till senescence. Spermatogenesis occurs along the length of the seminiferous tubules, and the process may be divided into three phases: (1) Mitotic divisions of spermatogonia generate the spermatocytes, which are destined to turn out to be mature sperm; (2) meiotic divisions of the spermatocytes, which lower the chromosome number and produce haploid spermatids; and (3) spermiogenesis, during which spermatids are remodeled into mature sperm through the lack of cytoplasm and the development of flagella. There is a temporal organization to the spermatogenic cycle, called the spermatogenic wave, which ensures that mature spermatozoa are produced constantly. Two million spermatogonia start this course of day by day, and since every spermatogonium gives rise to sixty four spermatozoa, 128 million sperm are produced day by day. Storage of Sperm, Ejaculation, and Function of Sex Accessory Glands Sperm go away the testes through ducts that carry them to the epididymis, the first location for the maturation and storage of sperm. During sexual arousal, contractions of the graceful muscle across the ducts advance sperm through the epididymis. At ejaculation, sperm are expelled into the vas deferens after which into the urethra. The ampulla of the vas deferens supplies one other storage area for sperm and secretes a fluid rich in citrate and fructose, which nourishes the ejaculated sperm. The seminal vesicles secrete a fluid rich in fructose, citrate, prostaglandins, and fibrinogen. As the vas deferens empties its sperm into the ejaculatory duct, every seminal vesicle contributes its secretions, which additionally will be nutritive for the ejaculated sperm. The prostaglandins present in seminal fluid might assist in fertilization in two methods: (1) Prostaglandins react with cervical mucus to make it more penetrable by sperm, and (2) prostaglandins induce peristaltic contractions within the female reproductive tract. The prostate gland provides its own secretion to the ejaculate, a milky aqueous solution rich in citrate, calcium, and enzymes. The prostatic secretion is barely alkaline, which will increase sperm motility and aids in fertilization by neutralizing acidic secretions from the vas deferens and the vagina. Collectively, the combined secretions of the male intercourse accessory glands compose ninety% of the amount of semen, and sperm compose the remaining 10%. Normally, the testes occupy the scrotum, which lies exterior the physique cavity and is maintained at 35°C36°C, or 1°C2°C under physique temperature.
In some instances symptoms 7 generic 10 mg benazepril amex, newly seeded cancer cells must survive and increase in naпve medications ordered po are order benazepril with visa, fully regular tissue microenvironments treatment of chlamydia generic benazepril 10 mg on line. In different instances, the newly encountered tissue microenvironments may already be supportive of such disseminated cancer cells, having been preconditioned previous to their arrival. Cancer Cells, Cancer Stem Cells, and Intratumoral Heterogeneity Cancer cells are the muse of the illness. They provoke neoplastic development and drive tumor development ahead, having acquired the oncogenic and tumor suppressor mutations that outline cancer as a genetic illness. Traditionally, the cancer cells inside tumors have been portrayed as moderately homogeneous cell populations till comparatively late in the middle of tumor development, when hyperproliferation mixed with increased genetic instability spawn genetically distinct clonal subpopulations. An elaborate integrated circuit working inside regular cells is reprogrammed to regulate the hallmark capabilities acquired by cancer cells (A) and by related stromal cells. Separate subcircuits, depicted right here in differently colored fields, are specialised to orchestrate distinct capabilities. The abundance, histologic organization, and characteristics of the stromal cell types and related extracellular matrix (hatched background) evolves during development, thereby enabling main, invasive, and then metastatic growth. These, typically uncommon, tumor-initiating cells have proven to share transcriptional profiles with certain regular tissue stem cells, thus justifying their designation as stemlike. Another form of phenotypic variability resides in the genetic heterogeneity of cancer cells inside a tumor. Genomewide sequencing of cancer cells microdissected from different sectors of the same tumor145 has revealed putting intratumoral genetic heterogeneity. Some of this genetic diversity could also be reflected in the long recognized histologic heterogeneity inside particular person human tumors. Thus, genetic diversification may produce subpopulations of cancer cells that contribute distinct and complementary capabilities, which then accrue to the widespread advantage of general tumor growth, development, and resistance to remedy, as described earlier. Alternatively, such heterogeneity may merely reflect the genetic chaos that arises as tumor cell genomes turn into more and more destabilized. Instead, we think about how the outline of hallmark principles is likely to inform therapeutic development at current and may more and more achieve this sooner or later. Thus, the rapidly rising armamentarium of therapeutics directed against specific molecular targets could be categorized according to their respective results on one or more hallmark capabilities, as illustrated in the examples presented in Figure 2. Indeed, the observed efficacy of these medication represents, in each case, a validation of a particular capability: If a capability is actually important to the biology of tumors, then its inhibition should impair tumor growth and development. Unfortunately, nevertheless, the clinical responses elicited by these targeted therapies have usually been transitory, being followed all too typically by relapse. One interpretation, which is supported by rising experimental evidence, is that each of the core hallmark capabilities is regulated by a set of partially redundant signaling pathways. Consequently, a targeted therapeutic agent inhibiting one key pathway in a tumor may not fully get rid of an indicator capability, allowing some cancer cells to survive with residual function till they or their progeny finally adapt to the selective stress imposed by the initially utilized remedy. Such adaptation can reestablish the expression of the practical capability, allowing renewed tumor growth and clinical relapse. Because the variety of parallel signaling pathways supporting a given hallmark should be limited, it could turn into potential to therapeutically cotarget all of these supporting pathways, thereby stopping the development of adaptive resistance. Another dimension of the plasticity of tumors underneath therapeutic attack is illustrated by the unanticipated responses to antiangiogenic remedy, by which cancer cells reduce their dependence on this hallmark capability by increasing their dependence on another. Thus, many observers anticipated that potent inhibition of angiogenesis would starve tumors of significant nutrients and oxygen, forcing them into dormancy and probably leading to their dissolution. Drugs that intervene with each of the hallmark capabilities and hallmarkenabling processes have been developed and are in preclinical and/or clinical testing, and in some instances, approved for use in treating certain types of human cancer. A concentrate on antagonizing specific hallmark capabilities is likely to yield insights into developing novel, highly efficient therapeutic strategies. The initial clinical validation of this adaptive/evasive resistance is clear in the increased invasion and local metastasis seen when human glioblastomas are treated with antiangiogenic therapies. Analogous adaptive shifts in dependence on different hallmark traits may also limit the efficacy of analogous hallmark-focusing on therapies.