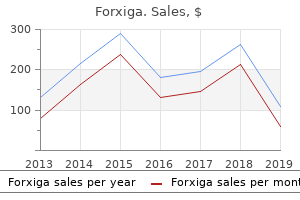
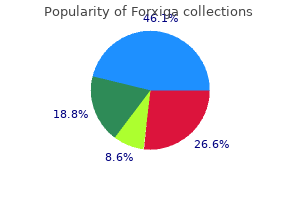
Forxiga
"Discount forxiga 5mg mastercard, diabetes test results pregnancy".
By: E. Marlo, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, Albert Einstein College of Medicine
Weakness diabetes type 1 ketones order 5 mg forxiga with amex, atrophy diabetes a1c forxiga 10 mg without a prescription, and reflex loss without sensory change are the primary features and are mentioned in detail in Chap signs juvenile diabetes babies quality forxiga 5 mg. A few patients suspected of getting childish or childhood muscular atrophy prove, with the passage of time, to be merely inactive "slack" youngsters, whose motor growth has proceeded at a slower rate than regular. These quantity of|various|a variety of} other|and a number of} other} different congenital myopathies- central core, rod-body, nemaline, mitochondrial, myotubular, and fiber-type disproportion and predominance- are described in Chap. Unlike WerdnigHoffmann illness, the effects of lots of them are likely to|are inclined to} diminish because the natural progress of muscle proceeds. Rarely, polymyositis and acute idiopathic polyneuritis manifest themselves as a syndrome of congenital hypotonia. Infantile muscular dystrophy and lipid and glycogen storage diseases may also produce a scientific image of progressive atrophy and weak point of muscle tissue. The diagnosis of glycogen storage illness (usually the Pompe form) ought to be suspected when progressive muscular atrophy is associated with enlargement of the tongue, coronary heart, liver, or spleen. Certain forms of muscular dystrophy (myotonic dystrophy quantity of|various|a variety of} other|and a number of} other} forms of congenital dystrophy) may also be evident at start or quickly thereafter. All of those issues are described in detail in the chapters on muscle diseases. Brachial plexus palsies, well-known complications of dystocia, normally result from forcible extraction of the fetus by traction on the shoulder in a breech presentation or from traction and tipping of the pinnacle in a shoulder presentation. Their neonatal onset is betrayed later by the small dimension and inadequate osseous growth of the affected limb. Either the higher brachial plexus (fifth and sixth cervical roots) or the decrease brachial plexus (seventh and eighth cervical and first thoracic roots) endure the brunt of the injury. Upper plexus injuries (Erb) are about 20 times more frequent than decrease ones (Klumpke). Facial paralysis, forceps injury to the facial nerve immediately distal to its exit from the stylomastoid foramen is one other common (usually unilateral) peripheral nerve affection in the newborn. Failure of 1 eye to shut and problem in sucking make this condition simple to recognize. Ё In most circumstances of facial paralysis physical injury, operate is recovered after a few of} weeks; in some, the paralysis is everlasting and may account for lifelong facial asymmetry. Treatment Assistive units, stretching remedy, and conventional orthopedic measures for joint stabilization and relief of spasticity are all helpful. Most published trials have been too small, nonetheless, to enable firm conclusions to be drawn about the sturdiness of this remedy. Finally, hyperbaric oxygen remedy of youngsters with cerebral palsy was not effective in a randomized trial conducted by Collet and colleagues, regardless of periodic claims to the opposite. In summary, might be} stated that each one|that every one} these forms of disabling motor abnormalities rank high as important points in neuropediatrics. In attempts at prevention, steps have been taken in most hospitals to establish and remove risk elements. Indeed, higher prenatal care, reduction in untimely births, and control of respiratory problems in crucial care wards have decreased their incidence and prevalence. Physical and psychological therapeutic measures appear to be useful, however many of the methods have been difficult to consider in a nervous system present process maturation and growth. The neurologist can contribute most by segregating teams of circumstances of similar sample and etiology and in differentiating the congenital teams of delayed expressivity from the treatable acquired diseases of this age interval. We embrace a dialogue of those intrauterine infections right here some of them could result in malformations or harmful lesions of the brain and, later in life, have to be distinguished from developmental abnormalities. The rubella virus enters embryonal tissues during the first trimester, Treponema pallidum in the fourth to fifth postconceptional months, and Toxoplasma after that interval. Bacterial meningitis (except for that Listeria monocytogenes, described below) is actually a paranatal infection contracted during or immediately after parturition. Neonatal herpes simplex encephalitis, the type 2 (genital) virus, additionally be|can be} normally acquired by passage by way of an contaminated start canal. Nevertheless, on scientific grounds alone, certain infections can be identified and others excluded. Thus, there are scientific signposts to information the clinician in selecting the suitable diagnostic checks. And importantly, in considering neonatal infections, one should also search for different, less common infectious varieties (see Chaps. Added problem in the diagnosis of embryonal and fetal infections arises when the mother has been entirely asymptomatic.
As noted diabetes type 1 risk factors cheap 10mg forxiga with mastercard, partial seizures differ with the locale of the lesion and are conventionally divided into two groups diabetes log sheet discount forxiga 10 mg mastercard, easy and complicated diabetes mellitus ppt buy forxiga 5mg low cost, relying on whether or not consciousness is retained or impaired. Complex partial seizures most frequently have their focus in the temporal lobe on one side or the other, however a frontal localization additionally be|can be} well known. The sites of the offending lesions and the kinds of seizures to which they provide rise are listed in Table 16-2. These relationships are so helpful in diagnosis that they should to} be familar to all neurologists. Frontal Lobe Partial Seizures (Focal Motor and Jacksonian Seizures) Focal or partial motor seizures are attributable to a discharging lesion of the opposite frontal lobe. The most typical sort, originating in the supplementary motor space, takes the form of a turning motion of the top and eyes to the side reverse the irritative focus, often associated with a tonic contraction of the trunk and limbs on that side. This might represent the entire seizure, or it may be adopted by generalized clonic actions; the extension of the seizure might happen simply before or concurrently with loss of consciousness. On the other hand, a lesion in a single frontal lobe might give rise to a serious generalized convulsion with out an initial turning of the top and eyes. Since the turning actions are usually to the side reverse the irritative focus (sometimes to the identical side), contraversive and ipsiversive, respectively, can be preferable phrases. The similar is true for the top and eye turning that happens on the end of the generalized tonic-clonic part of versive seizures (Wylie et al). Contraversive deviation of only the top and eyes may be induced most consistently by electrical stimulation of the superolateral frontal area (area 8), simply anterior to space 6 (see Fig. Less dependably, the identical actions may be obtained by stimulating the more anterior parts of the frontal cortex, or the supplementary motor space, and the temporal or occipital cortex- presumably via propagation of the ictal discharge to the frontal contraversive space. In seizures of temporal lobe origin, early in the seizure, there additionally be} head turning ipsilaterally adopted by forceful, contraversive head (and body) turning. These head and body actions, in the event that they} happen, are preceded by quiet staring and other automatisms. The jacksonian motor seizure begins with a tonic contraction of the fingers of one hand, the face on one side, or the muscle tissue of one foot. This transforms into clonic actions in these components in a trend analogous to that in a generalized clonic-tonic-clonic convulsion. Sometimes a series of clonic actions of accelerating frequency build up to as} a tonic contraction. The actions might stay localized or unfold ("march") from the part first affected to other muscle tissue on the identical side of the body. In the latter, or "traditional," jacksonian kind, which is comparatively uncommon, the seizure spreads from the hand, up the arm, to the face, and down the leg; or, if the primary motion is in the foot, the seizure marches up the leg, down the arm, and to the face, usually in a matter of 20 to 30 s. In some cases, the one-sided seizure exercise is adopted by turning of the top and eyes to the convulsing side, often to the opposite side, and then by a generalized seizure with loss of consciousness. Following convulsions which have a outstanding focal motor signature, there additionally be} a transient paralysis of the affected limbs. Continued focal paralysis past this time usually indicates the presence of a focal brain lesion as the underlying explanation for the seizure. A comparable phenomenon is present in cases of focal epilepsy that contain the language, somesthetic, or visible areas; here the persistent deficit corresponds to the area of brain affected. The high incidence of onset of focal motor epilepsy in the face, hands, and toes is probably related to the disproportionately giant cortical illustration of these components. The disease course of or focus of excitation is usually in or near the rolandic (motor) cortex, i. Lesions confined to the motor cortex are reported to assume the form of clonic contractions, and people confined to the premotor cortex (area 6), tonic contractions of the contralateral arm, face, neck, or all of one side of the body. Perspiration and piloerection happen often in components of the body concerned in a focal motor seizure, suggesting that these autonomic features have a cortical illustration in or adjoining to the rolandic space. Focal motor and jacksonian seizures have primarily the identical localizing significance. Seizure discharges arising from the cortical language areas might give rise to a quick aphasic disturbance (ictal aphasia) and ejaculation of a word, or, more regularly, a vocal arrest. Ictal aphasia is usually succeeded by other focal or generalized seizure exercise however might happen in isolation, with out loss of consciousness, during which case it can possibly} later be described by the patient. These disturbances must be distinguished from the stereotyped repetition of words or phrases or the garbled speech that characterizes some cases of advanced partial seizures or the postictal confusional state. As identified by Manford and colleagues, comparatively few focal seizures may be localized precisely from scientific data alone.
5 mg forxiga amex. Live Well with DIABETES - Public Forum Launch 2/11/2019.
Nor is it clear that the dilatation of 1 pupil is all the time due to of} blood sugar 44 buy forxiga without a prescription compression of the oculomotor nerve by the herniated uncus diabetes 1 and 2 generic forxiga 5 mg visa, as historically taught diabetes type 2 research studies order forxiga now. Involvement of the third nerve nucleus or its fibers of exit may be be} answerable for the dilatation of the other pupil, the same old} occurrence after the pupil on the aspect of the mass has turn out to be fastened (Ropper 1990). In our serial study of 12 sufferers with mind edema and lateral diencephalic-mesencephalic shifts due to of} hemispheral infarcts, four sufferers initially had no ipsilateral pupillary enlargement; in 1 patient, the pupillary enlargement was contralateral; in three sufferers, the pupils were symmetrical when drowsiness gave method to stupor or coma (Ropper and Shafran). In one patient, the first motor sign was an ipsilateral decerebrate rigidity quite than decorticate posturing; many of the sufferers had bilateral Babinski signs by the point they became stuporous. Indeed, the appearance of a Babinski sign on the nonhemiparetic aspect has been probably the greatest sentinels of secondary mind tissue shift. These signs normally progressed to deep coma and decerebration within hours, and so they fluctuated. Moreover, the early disturbances of consciousness (drowsiness and stupor) dependably observe the degree of lateral displacement of excessive brainstem and subthalamic structures (judged by shifts in the position of midline structures such because the pineal physique and, with less accuracy, the septum pellucidum), all of which may occur in the absence of transtentorial herniation, which arises later. The necessary parts of secondary compression of the upper brainstem, actually, occur above the plane of the tentorium. With acute lots, a 3- to 5-mm horizontal displacement of the pineal calcification is related to drowsiness; 5 to 8 mm, with stupor; and higher than 8 or 9 mm, with coma (Ropper, 1986). Others, notably Reich and colleagues, discover the evidence for vertical shift to be more compelling than for horizontal displacement. The location properly as|in addition to} the dimensions of a mass determines the degree of mind distortion and displacement of crucial structures in the decrease diencephalon and upper midbrain. Andrews and colleagues have pointed out that frontal and occipital hemorrhages are less more likely to|prone to} displace deep structures and to cause coma than are clots of equal measurement in the parietal or temporal lobes. Nor is it shocking that slowly enlarging lots, corresponding to mind tumors, could typically cause large shifts of mind tissue yet result in few scientific changes. In other phrases, all of the above comments pertain solely to structural changes that are be} acute. Sometimes the primary disorder is perfectly apparent, as with extreme cranial trauma. The need for effectivity in reaching a analysis and providing appropriate acute care demands that the doctor have a methodical method that leaves none of the the} widespread and treatable causes of coma unexplored. If hypotension is present, certain therapeutic measures- placement of a central venous line and administration of fluids and pressor brokers, oxygen, blood, or glucose options (preferably after blood is drawn for glucose determinations and thiamine is administered)- take precedence over diagnostic procedures. Deeply comatose sufferers with shallow respirations require endotracheal intubation. The patient with a head damage can also have suffered a fracture of the cervical vertebrae, in which case warning have to be exercised in shifting the pinnacle and neck properly as|in addition to} in intubation, lest the spinal wire be inadvertently damaged. These matters are mentioned in higher detail further on, underneath "Management of the Acutely Comatose Patient. A massive class of compounds could scale back alertness to the purpose of profound somnolence or stupor, particularly if there are underlying medical problems (especially liver failure). Prominent in lists of iatrogenic drug intoxications are anesthetics, sedatives, anticonvulsants, opiates, antidepressants, and a few antipsychotic compounds. Chronic administration of nitroprusside for hypertension can induce stupor from cyanide toxicity. From an initial survey, most of the widespread causes of coma- corresponding to extreme head damage, alcoholic or other forms of drug intoxication, and hypertensive mind hemorrhage- are readily acknowledged. General Examination Alterations in important signs- temperature, pulse, respiratory rate, and blood pressure- are necessary aids in analysis. Fever is most often due to of} a systemic an infection corresponding to pneumonia or to bacterial meningitis or viral encephalitis. An excessively excessive physique temperature (42 or forty three C) related to dry skin ought to arouse suspicion of heat stroke or intoxication by a drug with anticholinergic activity. Hypothermia is noticed in sufferers with alcoholic or barbiturate intoxication, drowning, exposure to chilly, peripheral circulatory failure, and myxedema. Slow breathing points to opiate or barbiturate intoxication and occasionally to hypothyroidism, whereas deep, fast breathing (Kussmaul respiration) ought to counsel the presence of pneumonia, diabetic or uremic acidosis, pulmonary edema, or the less widespread occurrence of an intracranial illness that causes central neurogenic hyperventilation. Diseases that elevate intracranial stress or injury the mind often cause gradual, irregular, or cyclic CheyneStokes respiration (see further on). The numerous disordered patterns of breathing and their scientific significance are described further on and on page 474.
Fasciculation potentials in lesser numbers are additionally noticed with continual nerve entrapments diabetes mellitus news purchase forxiga 10 mg on-line. In all these circumstances diabetes insipidus electrolyte abnormalities discount forxiga 5mg without a prescription, the damaged neuron or its axon appears to blood glucose xls purchase genuine forxiga on line go away intact axons in a state of hyperirritability. The small motor unit discharges might occur singly or as doublets, triplets, or multiplets. The web site of generation of this activity has additionally been contested, possibly outcome of|as a result of} it might arise from a number of} sites, but all the time the location is peripheral, not central, and is believed to correspond to an alteration in the calcium focus in the microenvironment of the motor axon. Spontaneous discharges arising in large myelinated fibers have been implicated in the genesis of myokymia; certainly, demyelinating polyneuropathies are among the many conditions that give rise to this phenomenon. Myokymia brought on by peripheral nerve hyperexcitability each potassium channel mutations and antibodies against the channels. This activity blocked by lidocaine infusion across the peripheral nerve and diminished by carbamazepine or phenytoin. Focal and segmental myokymias differ in small ways from the generalized type of myokymia with regard to the timing and du- ration of the discharges. The focal varieties refer primarily to facial myokymia, seen most often in quantity of} sclerosis, Guillain-Barre synґ drome, large cerebellopontine angle tumors, or compression of the facial nerve by a small aberrant blood vessel, but it might follow any peripheral nerve damage and regeneration. Segmental myokymia is a typical prevalence in radiation injuries of the brachial plexus. The origin of these discharges (also referred to as neuromyotonia) might be in the distal peripheral nerve, the place activity of afferent fibers, possibly through ephaptic transmission, irregularly excites distal motor terminals. Segmental myokymia refers to similar activity in the distribution of quantity of} adjacent motor roots. The phenomenon of myotonia, which denotes a failure of voluntary relaxation of muscle due to sustained firing of the muscle membrane (see pages 1265 and 1270), is characterised by highfrequency repetitive discharges usually having a positive sharp waveform. These myotonic discharges wax and wane in amplitude and frequency, producing a "dive-bomber" sound on the audio monitor. The discharges may be elicited mechanically by percussion of the muscle or movement of the needle electrode and are additionally seen following voluntary contraction or electrical stimulation of the muscle through its motor nerve. If the muscle is activated repeatedly at short intervals, the late discharge becomes briefer and briefer and finally disappears (see Fig. The five strains are a steady record of activity in the biceps brachii following a faucet on the tendon. They are seen in some myopathies, in hypothyroidism, and in sure denervating issues and are a mark of chronicity (lesions over 6 months old). High-frequency coupling of action potentials into doublets, triplets, or larger multiples of single units, indicating instability in repolarization of the nerve fiber to a muscle, happens in tetany and in the early stages of myokymia. The cramp-like contracture of McArdle illness and phosphofructokinase deficiency is related to electrical silence of contracting muscle. This function is a crucial part of of} the definition of true physiologic muscle contracture (as distinguished from continual shortening of a muscle and its tendon which, strictly talking, is a pseudocontracture). Presumably, new nerve twigs have sprouted from nodal factors and terminals of undamaged axons and have reinnervated previously denervated muscle fibers, thus adding them to their own motor units. Increased amplitude is often related to very continual, proximal axon loss. The shaded muscle fibers are practical members of 1 motor unit, whose axon enters from the higher left and branches terminally to innervate the suitable muscle fibers. The action potential produced by every motor unit is seen in the higher right: its duration is measured between the 2 vertical strains. In this myopathic unit, only two fibers remain lively; the opposite three (shrunken) have been affected by one of many primary muscle diseases. Four fibers which originally belonged to different motor units and had been denervated have now been reinnervated by terminal sprouting from an undamaged axon. Note that only underneath these abnormal circumstances do fibers in the same unit lie next to one another.