Retrovir
"Buy retrovir master card, treatment math definition".
By: S. Larson, M.A.S., M.D.
Professor, Creighton University School of Medicine
Cyclosporine-mediated vasoconstriction of the microvasculature accounts for a characteristic occlusive arteriolopathy and subsequent tubular epithelial cell damage medicine park lodging cheap retrovir 300mg with visa. A principal aspect effect of antineoplastic brokers is direct tubular toxicity with the clinical features of acute renal failure medications every 8 hours cheap retrovir express. An invariable concern in all such cases is the consequently prolonged half-lifetime of the brokers administered and their increased tendency to treatment jokes order retrovir no prescription systemic toxicity. Major sources of lead exposure are lead-based mostly paints, lead leached into food throughout storage or processing, significantly in residence-brewed unlawful alcoholic drinks (moonshine), and increasingly, environmental exposure (gasoline, industrial fumes). This insidious accumulation of lead has been implicated within the etiology of a syndrome of hyperuricemia, hypertension, and progressive renal failure. As may be expected from its association with elevated blood pressure, hypertensive vascular modifications are a outstanding characteristic of the kidney in these cases. Acute lead intoxication is rare however may be encountered after unintentional ingestion, usually by children. Its principal manifestations are stomach colic, hemolytic anemia, and encephalopathy. Tubular degeneration, interstitial fibrosis, and mononuclear cell infiltration are central components of damage to the kidney by vascular diseases that affect the intrarenal circulation. In rare situations in which the onset of the vascular illness is sudden and severe, corresponding to fulminant vasculitis, the kidney lesions are those of infarction and are related to acute renal failure. Tubular damage and interstitial mobile infiltrates are some of the earliest responses to any physical impedance to the flow of urine (see Chapter 108). Early aid of the obstruction, inside this relatively brief interval, can lead to stabilization and reversal of renal failure. Persistence of the obstruction will result in irreversible fibrosis and progressive renal failure. Infection is a traditional, however not invariable characteristic of most forms of obstructive nephropathy. In reality, with few exceptions, urinary an infection will ultimately develop in most sufferers with urinary tract obstruction. In such cases, an infection will contribute significantly to the symptomatology and can aggravate the progression to renal insufficiency. Those brought on by hypercalcemia and potassium depletion are mainly useful in nature and reversible if corrected early. The kidneys are the most important organs of urate excretion and a principal goal of its irregular metabolism (see Chapter 299). The renal lesions end result either from the intratubular crystallization of uric acid within the low pH of the distal tubules (acute urate nephropathy, uric acid nephrolithiasis) or from the deposition of amorphous tophi of sodium urate within the renal parenchyma (persistent urate nephropathy). Acute urate nephropathy develops when nucleoprotein launch following huge cell damage (tumor lysis syndrome, rhabdomyolysis) in a setting of quantity depletion causes a sudden overproduction of urate that ends in an acute progressive deterioration in renal perform and oliguria. The serum urate focus is usually larger than 20 mg/dL, and the ratio of the focus of uric acid to that of creatinine is bigger than 1 in a spot urine sample. The hyperphosphatemia and hyperkalemia are the result of the cell necrosis that also accounts for the hyperuricemia. The hypocalcemia is consequent to the precipitation of calcium at sites of damage the place in situ concentrations of the launched intracellular phosphate are excessive. Treatment consists of quantity substitute sufficient to maintain a excessive urine flow rate, which washes out urate precipitates and reduces the urinary focus of urate; alkalinization of the urine, which increases the solubility of uric acid; and discount of the excreted urate load by blocking its manufacturing with allopurinol. The latter type is extra frequent in overproducers of uric acid and in those that have a defect in their capability to improve ammonia manufacturing in response to an acid load. Uric acid nephrolithiasis is frequent in these people, whose urinary excretion of uric acid is elevated even within the presence of regular blood levels. Intratubular uric acid precipitates could be also a nidus for calcium oxalate stones, which are frequent in these people. Renal failure on account of intrarenal gouty tophi is rare however can happen in those with chronically elevated serum urate levels of greater than 10 mg/dL in women and 13 mg/dL in men. Increased renal excretion of the metabolic finish product oxalate ends in its intratubular precipitation as calcium oxalate. Acquired forms of hyperoxaluria are secondary to ingestion or exposure to oxalate precursors (ethylene glycol, methoxyflurane anesthesia, ascorbic acid, pyridoxine deficiency) or increased intestinal absorption of oxalate (regional enteritis, small bowel resection).
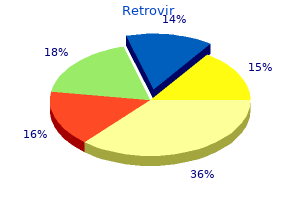
Usage: t.i.d.
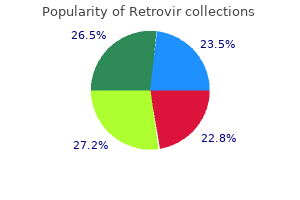
Correction of the precipitating factor(s) sometimes permits gradual return to medicine in spanish retrovir 300 mg lowest price a subclinical stage of hepatic encephalopathy 7 medications emts can give buy retrovir on line. This type of hepatic encephalopathy is extremely troublesome to silent treatment discount retrovir 100 mg fast delivery handle because of its resistance to conventional therapy and food regimen restrictions. Hepatocerebral degeneration is a continual unremitting motor dysfunction of variable severity (tremor, rigidity, hyperreflexia, or signs of advanced pyramidal, extrapyramidal, and cerebral dysfunction) along with recurrent episodes of traditional overt hepatic encephalopathy. This extremely rare dysfunction usually occurs in patients with huge portosystemic shunts (often surgically created); it responds poorly to therapy. Spastic paralysis, which is the least common presentation of hepatic encephalopathy, occurs solely not often in patients with continual hepatic encephalopathy and/or hepatocerebral degeneration; it also is very troublesome to deal with. Preclinical and gentle hepatic encephalopathy (stages zero-1, 1, 2) could be acknowledged by poor efficiency on psychometric exams. Clinically suspected hepatic encephalopathy may be objectively confirmed by extended reaction time to visible or auditory evoked potentials. Measurement of serum ammonia degree is non-delicate as a result of hepatic encephalopathy can happen in patients with a standard blood ammonia degree. Consistent with the current theories about the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy, there are four general targets/objectives of therapy: (1) intestines: decrease production and absorption of possible toxins; (2) liver: enhance liver function and clearance of poisons; (three) blood-brain barrier: prevent penetration of potential toxins into the brain; and (four) brain: appropriate irregular neuronal activity. The small and enormous intestines are the principle sources of ammonia and the other toxins which will cause hepatic encephalopathy. Lactulose is a non-absorbable disaccharide; by inflicting acidification of intestinal contents and performing as a cathartic agent, it decreases the absorption of ammonia into the blood stream. Lactulose could be given orally, via a nasogastric tube, or rectally (much less efficient) in doses of 30 to a hundred and twenty mL/day to produce two to four soft bowel actions per day. Poorly absorbed antibiotics, corresponding to neomycin (initially 1-2 g orally four occasions a day), alter intestinal flora and thus decrease the production of nitrogenous substances by micro organism and cut back the release of ammonia into the blood. Because continual neomycin can promote colonization with resistant organisms and may be absorbed systemically and cause nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, neomycin ought to be used for short intervals of time, and the dose ought to be decreased to 1 to 2 g/day after achievement of the desired medical effect. Alternatively, metronidazole could be given at 250 mg orally 3 times a day alone or with neomycin; the most typical unwanted side effects of continual metronidazole are peripheral neuropathy and dysgeusia. Dietary restriction of protein can decrease the production of ammonia by colonic micro organism. However, lengthy-time period dietary protein restriction can lead to malnutrition and could be harmful, especially in patients with decreased liver synthetic function. If tolerated, a constructive nitrogen steadiness might enhance hepatic encephalopathy by promoting hepatic regeneration and growing the capability of muscle to detoxify ammonia. Clinical trials are currently evaluating the function of supplementary zinc, which is a cofactor of urea cycle enzymes, and ornithine-aspartate, which may cut back blood ammonia by stimulating ureagenesis and synthesis of glutamine within the liver. Benzoate, which conjugates with glycine to kind hippuric acid, and phenylacetate, which conjugates with glutamine to kind phenylacetylglutamine, can present potential different pathways for the urinary excretion of nitrogen-containing molecules. Branched-chain amino acids (valine, leucine, isoleucine) given orally or parenterally can theoretically normalize the fragrant amino acid/branched-chain amino acid ratio and stop excessive penetration of fragrant amino acids into the brain. Flumazenil might transiently enhance the mental state in selected patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Prevention of clinically overt hepatic encephalopathy consists of early identification and timely correction of reversible precipitating elements, strict adherence to the food regimen, prevention of constipation, enchancment of liver function, and supportive therapy. Acute liver failure is a medical syndrome brought on by sudden, huge destruction of liver cells or by insults that severely inhibit the ability of hepatocytes to accomplish their normal features. The length of time that elapses between the medical recognition of liver illness and the onset of hepatic encephalopathy (and/or impairment of liver features) has been used to classify acute liver failure: inside 2 weeks-fulminant liver failure; inside 2 to eight weeks-subfulminant liver failure; and inside eight to 24 weeks-late onset liver failure. Patients with a shorter interval from the onset of jaundice to the event of hepatic encephalopathy generally have a better prognosis, with a decrease incidence of ascites however a higher incidence of cerebral edema compared with those that develop hepatic encephalopathy more slowly. Acetaminophen ingestion is answerable for 10% of acute liver failure instances within the United States. Massive liver cell necrosis from other medication corresponding to isoniazid, halogenated anesthetics, phenytoin, propylthiouracil, and sulfonamides accounts for an additional 10%; acute liver failure can also be induced by drug interactions, as seen with alcohol and acetaminophen, acetaminophen and isoniazid, and isoniazid and rifampin. A well-acknowledged cause of acute liver failure is ingestion of poisonous mushrooms (Amanita phalloides). There are an estimated 2000 instances of acute liver failure within the United States yearly, representing zero.
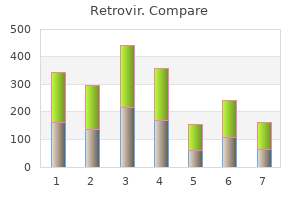
Immunodeficiency with elevated IgM stage is characterized by very low serum ranges of IgG and IgA but elevated stage of polyclonal IgM medicine xifaxan discount retrovir 100mg fast delivery. There is an increased frequency of autoimmune problems medications known to cause pill-induced esophagitis purchase 300 mg retrovir visa, similar to hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia; and transient medications of the same type are known as purchase cheap retrovir online, persistent, or cyclic neutropenia is common. Normal or solely slightly decreased numbers of B lymphocytes have been found within the blood of those sufferers. In the mid-1980s, cultured B cells from sufferers with X-linked hyper-IgM were shown to be capable of synthesizing IgA and IgG when co-cultured with a "switch" T-cell line, suggesting that the defect lay in T-lineage cells. The abnormal gene in X-linked hyper-IgM was localized to Xq26 and isolated in 1993. Thymic hypoplasia results from dysmorphogenesis of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches, leading to hypoplasia or aplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands. Other buildings forming at the similar age are additionally regularly affected, leading to anomalies of the nice vessels (proper-sided aortic arch), esophageal atresia, bifid uvula, congenital coronary heart illness (atrial and ventricular septal defects), a brief philtrum of the upper lip, hypertelorism, an antimongoloid slant to the eyes, mandibular hypoplasia, and low-set (often notched) ears. The prognosis is usually first advised by the presence of hypocalcemic seizures in the course of the neonatal period. A variable diploma of hypoplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands is extra frequent than complete aplasia. Some children with the features of this syndrome have little trouble with infections and present evidence of some cell-mediated immunity. Those with marked thymic hypoplasia may resemble infants with severe combined immunodeficiency in their susceptibility to infection with low-grade or opportunistic pathogens. Serum immunoglobulin ranges are usually regular for age, but these of some fractions, particularly IgA, could also be diminished and the IgE stage could also be elevated. Responses of peripheral blood lymphocytes following mitogen stimulation have been absent, decreased, or regular. Lymphoid follicles usually seem regular, but lymph node paracortical areas and thymus-dependent regions of the spleen present variable levels of depletion, depending upon the diploma of thymic hypoplasia. Familial incidence is uncommon, but three cases of apparent autosomal dominant inheritance have been reported. Other deletions associated with DiGeorge and velocardiofacial syndromes have been recognized on chromosome 10p13 (Table 272-1). In addition, serum immunoglobulin concentrations are diminished, and no antibody formation occurs after immunization. Use of those agents solely heightens the chance of demise from opportunistic infection. The shared gamma chain capabilities each to enhance the affinity of the receptor for the respective cytokine and to enable the receptors to mediate intracellular signaling. These mutations resulted in abnormal gammac chains in two thirds of the cases and absent gammac protein within the remainder. Milder forms of this situation have been reported, leading to delayed prognosis of immunodeficiency even to maturity. The latter instantly or indirectly results in T-cell apoptosis, which causes the immunodeficiency. The reason for that is unknown but is believed to be associated to the defective perform of the multiple forms of cytokine receptors that share gammac. Such mutations result in a practical incapability to type antigen receptors by way of genetic recombination. In 1959, similar twin male infants who exhibited a complete lack of each lymphocytes and granulocytes in their peripheral blood and bone marrow were described. Seven of eight infants reported died between ages three and 119 days from overwhelming infections; the eighth underwent complete immunologic reconstitution from bone marrow transplantation. Serum immunoglobulin numbers could also be regular or elevated for all classes, but selective IgA deficiency, marked elevation of IgE, and elevated IgD stage have been found in some cases. Studies of cellular immune perform have shown delayed cutaneous anergy to ubiquitous antigens, lymphopenia, and extremely low but not absent lymphocyte proliferative responses to mitogens and allogeneic cells in vitro. Peripheral lymphoid tissues usually reveal paracortical lymphocyte depletion. Most sufferers have regular or elevated concentrations of all serum immunoglobulins. This situation is invariably deadly in childhood until immunologic reconstitution could be achieved. Bone marrow transplantation is the remedy of selection but has up to now been successful in solely three such sufferers.